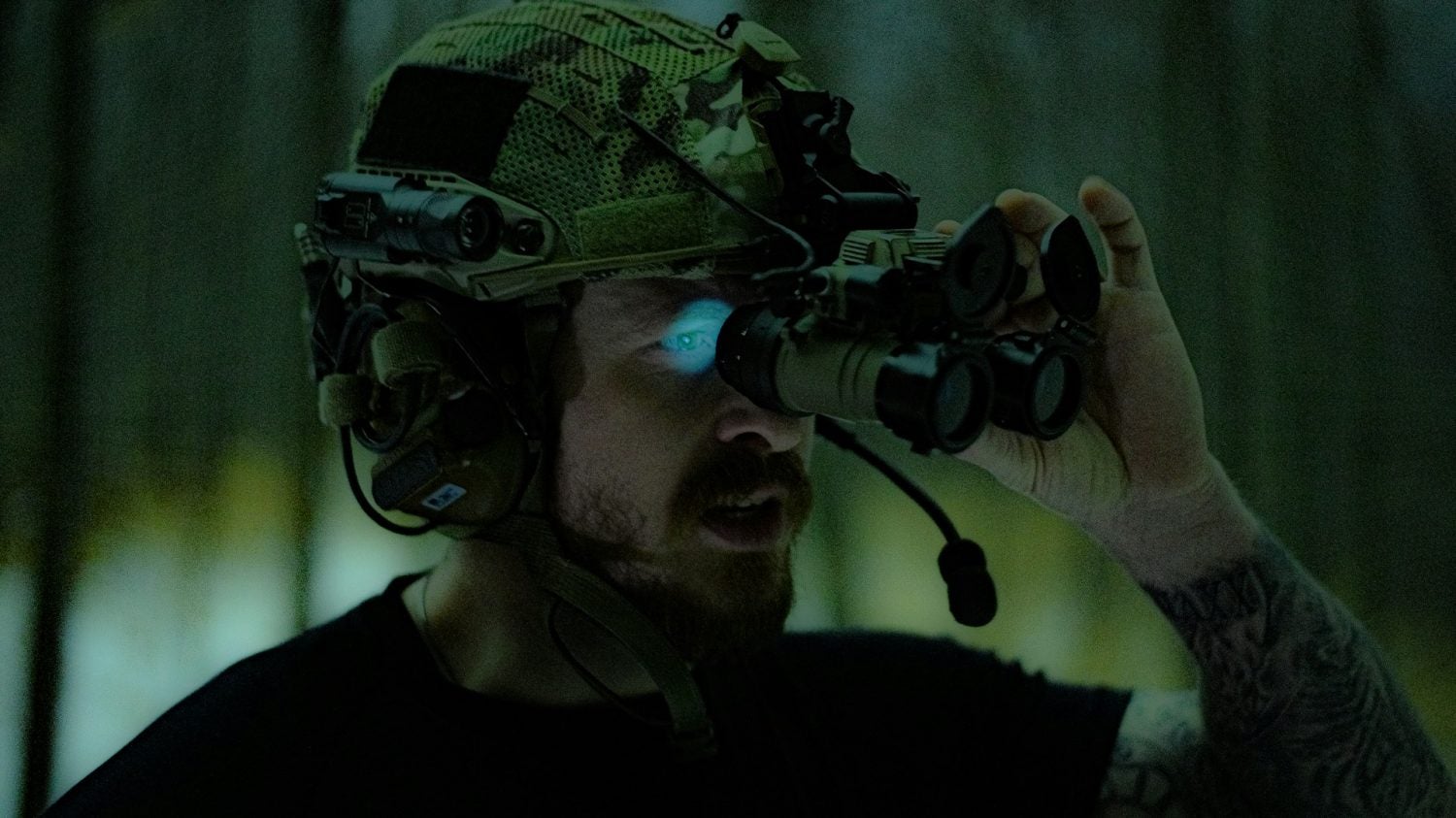
Tactical night vision technology has revolutionized security and surveillance operations, providing enhanced visibility and situational awareness in low-light or nighttime environments.
This article explores the art of tactical night vision’s evolution, applications, benefits, and considerations for practical use in security and surveillance settings.
Evolution of Night Vision Technology
The evolution of night vision technology spans several decades, marked by significant advancements in imaging capabilities, light amplification, resolution, and overall performance. Here are the key stages in the evolution of night vision technology:
First generation night vision (1940s-1960s)
Introduced during World War II, Gen 1 night vision relied on image intensifier tubes to amplify ambient light. These early systems produced a green-hued image with limited resolution and clarity.
Gen 1 technology enabled basic night vision capabilities for military use but significantly limited range and image quality.
Second generation night vision (1960s-1970s)
Gen 2 night vision represented a significant improvement over Gen 1 technology. It incorporated microchannel plates in image intensifier tubes, leading to higher light amplification, improved resolution, and brighter images.
Introducing ion barrier films enhanced performance, reducing halo effects and improving image clarity. Gen 2 systems became more widespread in military and law enforcement applications due to their superior performance compared to Gen 1.
Third-generation night vision (1970s-Present)
Gen 3 night vision marked a major performance and image quality leap forward. Advances in photocathode materials, such as gallium arsenide, resulted in higher sensitivity to low-light conditions and reduced noise levels.
Auto-gated technology was introduced, improving the ability to handle bright light sources without blooming or damaging the system. Gen 3 systems offer an extended operational range, clearer images, and enhanced reliability, making them the standard for military and professional use.
Ongoing developments in Gen 3 technology continue to improve performance, longevity, and adaptability to various operational environments.
Digital night vision (2000s-Present)
Digital night vision systems emerged in the 21st century, replacing traditional image intensifier tubes with digital sensors and displays. These systems offer the ability to record and store footage, digital zoom capabilities, and color imaging.
Digital night vision provides enhanced image processing, allowing for image enhancement, contrast adjustment, and customizable display settings. The integration of digital technology expands the versatility and functionality of night vision systems, catering to a wide range of applications beyond traditional low-light imaging.
Thermal imaging (1960s-Present)
In parallel with image intensifier-based night vision, thermal imaging technology rapidly developed.
Thermal imaging detects the infrared radiation that objects emit, creating heat-based images effective in total darkness, adverse weather conditions, and through obstacles such as smoke or foliage.
Thermal imaging systems offer detection capabilities beyond the visible spectrum, making them valuable for surveillance, search and rescue, and military reconnaissance. Advances in thermal imaging include higher-resolution sensors, improved image processing algorithms, and integration with other sensor technologies for comprehensive situational awareness.
Future trends and innovations
The ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the performance, reducing the size and weight, and improving the integration of night vision technology with other systems. Emerging trends include the development of ultra-sensitive sensors, advanced image processing algorithms, augmented reality overlays for night vision displays, and integrating night vision capabilities into wearable devices and unmanned systems.
As technology progresses, night vision systems are expected to become more versatile, user-friendly, and adaptable to various security, surveillance, and tactical applications across industries.
Benefits of Tactical Night Vision
Tactical night vision technology offers many benefits across various sectors and applications, revolutionizing operational capabilities, safety, and situational awareness in low-light or nighttime environments. Here are the key benefits of tactical night vision:
Enhanced visibility
One of the primary benefits of tactical night vision is its ability to provide clear visibility in low-light conditions, darkness, fog, smoke, and other challenging environments. It extends operational capabilities and effectiveness during nighttime operations, reducing reliance on ambient light sources.
Increased situational awareness
Tactical night vision enhances situational awareness by revealing threats, obstacles, and activities that may be obscured or invisible to the naked eye. It allows operators to proactively detect and respond to potential dangers, mitigating risks and improving decision-making.
Covert operations
Night vision technology enables covert operations and stealthy maneuvers by reducing adversaries’ visibility. It enhances operational security and mission success for military, law enforcement, and special forces engaged in undercover activities.
Improved target acquisition
Night vision aids in target acquisition by precisely imaging targets, even in low-light or obscured conditions. It enhances accuracy, reduces engagement times, and improves overall effectiveness in engagements and engagements.
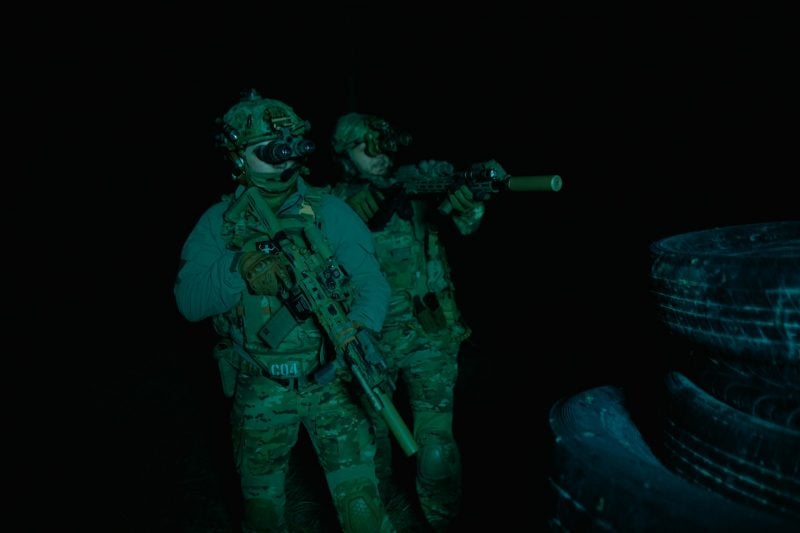

Reduced risk of accidents
Night vision technology helps mitigate the risk of accidents, collisions, and friendly fire incidents by providing clear visibility of personnel, vehicles, and hazards in low-light environments. It enhances safety for operators and minimizes the potential for unintended consequences during operations.
Flexibility and adaptability
Tactical night vision systems are versatile and adaptable to various operational scenarios, terrains, and mission requirements. They can be integrated with other sensors, weapons, and communication systems for comprehensive situational awareness and operational effectiveness.
Long-range detection
Advanced night vision systems offer long-range detection capabilities, allowing operators to detect and identify targets at extended distances in darkness. This capability is particularly valuable for surveillance, reconnaissance, and target acquisition missions.
Improved response times
Night vision technology enables faster response times to threats and emergencies by providing real-time imaging and actionable intelligence in low-light conditions. It enhances operational readiness and the ability to react swiftly to changing situations.
Versatility in environments
Tactical night vision systems are effective in various urban, rural, maritime, and wilderness settings. They perform well in adverse weather conditions, terrain obstacles, and low-visibility scenarios, ensuring operational effectiveness across diverse operational environments.
Training and skill development
Night vision technology facilitates training and skill development for operators by simulating realistic low-light scenarios, tactical engagements, and mission simulations. It enhances proficiency, decision-making, and operational readiness for night vision equipment personnel.
Considerations for Effective Night Vision Use
Effectively using night vision technology requires careful consideration of various factors to maximize performance, operational capabilities, and safety. Here are the critical considerations for effective night vision use:
Training and familiarization
Proper training and familiarization with night vision equipment are crucial for operators to understand its capabilities, limitations, maintenance procedures, and operational techniques. Training should include night vision fundamentals, equipment handling, troubleshooting, and tactical use in various scenarios.
Light management
Managing ambient light sources is essential for optimizing night vision performance. Avoiding bright light sources, such as headlights, flashlights, or artificial lighting, helps prevent blooming, glare, and image distortion that can degrade visibility. Utilize natural low-light conditions, moonlight, or starlight for improved imaging.
Maintenance and calibration
Regular maintenance, calibration, and quality control checks are necessary to ensure night vision systems operate at peak performance. Follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning, storage, battery maintenance, and sensor calibration to maintain image quality, focus, and reliability.
Battery management
Monitor battery levels closely and carry spare batteries or power sources to prevent equipment downtime during operations. Implement power-saving modes or settings to conserve battery life when maximum brightness is not required, extending operational duration in the field.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, precipitation, and terrain must be considered when using night vision technology. Extreme weather conditions, water exposure, dust, and debris can affect equipment performance and durability. Protective covers, cases, and environmental seals safeguard night vision systems.
Integration with other systems
Integrate night vision systems with complementary technologies, such as thermal imaging, laser rangefinders, GPS, and communication devices, for enhanced situational awareness and operational capabilities. Ensure seamless interoperability and compatibility between integrated systems for optimal performance.
Range estimation and target identification
Develop proficiency in range estimation and target identification techniques when using night vision systems. Understand the limitations of depth perception, magnification, and resolution in night vision imagery to assess distances and identify potential threats or targets accurately.
Elevate Your Security and Surveillance
Tactical night vision technology enhances security and surveillance by providing clear visibility, increased situational awareness, and operational advantages in low-light or nighttime environments.
Its evolution from traditional image intensifiers to modern digital and thermal imaging systems has expanded its applications across military, law enforcement, security, wildlife observation, and search and rescue domains.
Organizations and operators can leverage this technology to enhance their security strategies, improve response capabilities, and mitigate risks in challenging and dynamic environments by understanding the benefits, applications, and considerations for the effective use of tactical night vision.