For many years, cannabidiol (CBD) has been regarded as a go-to treatment for a wide range of health conditions, from muscle pain to cancer. It is in a class of compounds produced by the cannabis plant known as cannabinoids. Unlike recreational marijuana, CBD doesn’t trigger any psychoactive effects.
CBD is believed to have some health benefits, and because it is not psychoactive, the substance’s popularity has increased significantly in recent years.
What is CBD?
When hearing the term “cannabinoid,” most people immediately think of delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol or THC, which is also a cannabinoid like CBD and the most active ingredient in marijuana.
In addition to THC, marijuana also contains CBD and, while CBD is not psychoactive, it can bring about significant changes in the body. Most of these changes are beneficial, which is why CBD is widely used as a cure for medical conditions.
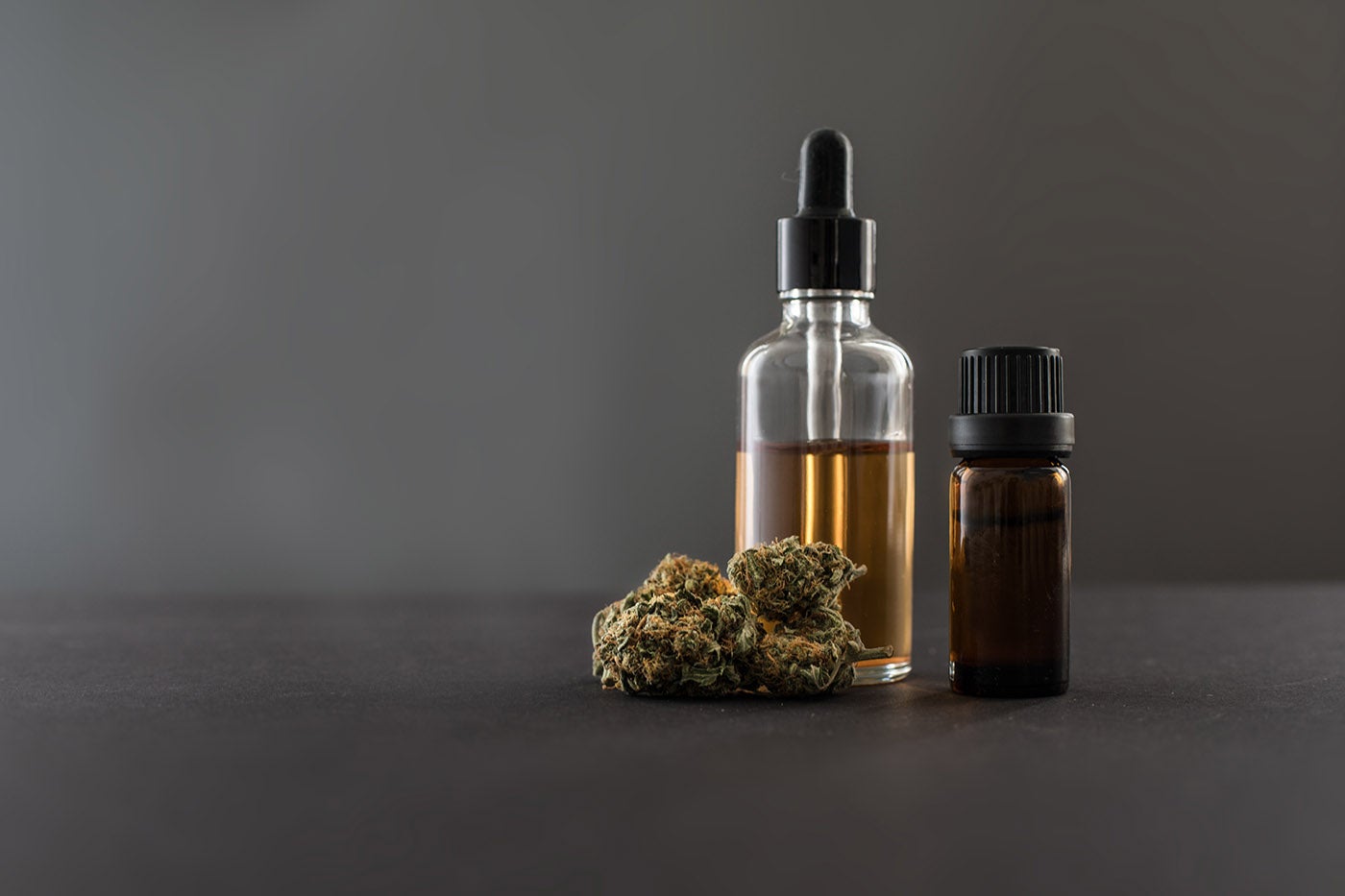
Most CBD oil for sale online comes from hemp, which is a form of the cannabis plant that undergoes minimal processing. Both hemp and marijuana come from the plant Cannabis Sativa. Marijuana farmers culture their plants to have a high THC content as well as other compounds they prefer to produce a particular smell or other characteristics.
The rise of hemp farming, specifically the farming of CBD-rich hemp, has given rise to companies selling CBD oil. One such company where you can buy pure CBD oil for sale is Royal CBD, a pioneer in the CBD-rich hemp industry.
Hemp, on the other hand, are not explicitly modified, and these are the plants that are used in the production of CBD oil.
THC and CBD are similar in several respects. Both compounds are cannabinoids, and they have the same chemical structure. The difference between THC and CBD lies in their atom arrangements and the receptors that interact with.
Effects of CBD on the Body
The Cannabis Sativa plant produces cannabinoids like THC and CBD, and they fall into the phytocannabinoid category. The body produces cannabinoids of its own, and they are called endocannabinoids.
Cannabinoids affect the body by attaching to receptors in the body’s endocannabinoid system. There are two types of receptors, namely CB1 receptors and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are located throughout the body, but they are prevalent in the brain.
CB1 receptors are responsible for a wide range of functions, including emotions, appetite, and coordination. THC has an affinity to react with these receptors, which typically triggers a psychoactive response.
CB2 receptors are more common in the immune system, and they are responsible for maintaining pain and inflammation. According to some studies, CBD reacts with CB2 receptors in the immune system to alleviate pain and other conditions like anxiety, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease. Because these receptors are not in the brain or elsewhere in the central nervous system, consuming CBD doesn’t result in a “high” or feelings of euphoria.
Some research has found that CBD doesn’t interact with CB2 receptors directly, but that it directs the endocannabinoid system to produce more endocannabinoids and address an endocannabinoid deficiency.
Health Benefits
Because CBD consumption can result in an increase of endocannabinoids without the psychoactive effects, there is a strong case for CBD and its health benefits.
Health benefits of CBD include natural pain relief, anti-inflammation, and anxiety reduction. In June 2018, the FDA approved the use of Epidiolex, which contains purified CBD for the treatment of epilepsy.
CBD is also believed to prevent cancer cells from spreading, and it can ease inflammation that causes Type 1 diabetes.
CBD is Marijuana Without the High
CBD is widely associated with marijuana, as it is a compound of the cannabis plant and an ingredient of marijuana. CBD also has a lot in common with THC, which is a psychoactive cannabinoid and the active ingredient of marijuana.
The difference between CBD and THC is that CBD doesn’t interact with receptors in the brain to cause psychoactive effects and, generally speaking, it is safe for consumption.